Fundamentals
What is a Database (DB) ?
- Any collection of related information
- DBs can be stored in different ways
Database Management Systems (DBMS)
A special software program that helps users create and maintain a database
- Makes it easy to manage large amounts of information
- Handles security
- Backups
- Importing/exporting data
- Concurrency
- Interacts with software applications (Programming Languages)
Common Operations (C.R.U.D)
- Create
- Read
- Update
- Delete
Two Types of Databases
- Relational Databases (SQL)
- Non-Relational Databases (NoSQL)
Relational Database Management Systems (RDBMS):
- MySQL
- Oracle
- PostgresSQL
- MariaDB
Non-Relational Database Management Systems (NRDBMS)
- MongoDB
- DynamoDB
- Apache Cassandra
- Firebase
Implementation specific, any non-relational database falls under this category, so there’s no set language standard. Most NRDBMS will implement their own language for performing C.R.U.D and administrative operations on the database.
Structured Query Language (SQL)
- Standardized language for interacting with RDBMS
- Used to perform C.R.U.D operations, as well as other administrative tasks (user management, security, backup, etc).
- Used to define tables and structures
- SQL code used on one RDBMS is not always portable to another without modification.
Database Queries
Queries are requests made to the database management system for specific information.
Tables and Keys
- Primary key: is a unique identifier for each record in a table.
- Surrogate key: is a unique identifier assigned to each record in a table to serve as its primary key. It is not derived from the data within the table and is typically a system-generated or sequentially assigned key for uniquely identifying records.
- Natural key: is a key in a database table that is derived from the data attributes of the entity it represents. It is based on existing data that already uniquely identifies each record, such as a person’s social security number or a product’s serial number.
A primary key can be used in the same table to create relationship between employees.
- Foreign key: is a field in a table that links to the primary key of another table.
- Composite key: is a key that consists of two or more columns in a table, used to uniquely identify each record when no single column uniquely identifies the records.
SQL Basics
SQL is actually a hybrid language, it’s basically 4 types of languages in one:
- Data Query Language (DQL)
- Used to query the database for information
- Get information that is already stored there
- Data Definition Language (DDL)
- Used for defining database schemas
- Data Control Language (DCL)
- Used for controlling access to the data in the database
- User & permissions management
- Data Manipulation Language (DML)
- Used for inserting, updating and deleting data from the database
Queries
A query is a set of instructions given to the RDBMS (written is SQL) that tell the RDBMS what information you want it to retrieve for you.
SQL Operation
Create, Delete and Update Tables
-- Different data types
INT -- Whole numbers
DECIMAL(M,N) -- Decimal values, exact value of numbers (4,3) - 1.023
VARCHAR(L) -- String of text of length L
BLOB -- Binary Large Object, stores large data
DATE -- 'YYYY-MM-DD'
TIMESTAMP -- 'YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS'CREATE TABLE student (
student_id INT AUTO_INCREMENT,
name VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL,
major VARCHAR(20) UNIQUE,
-- major VARCHAR(20) DEFAULT 'Undecided',
PRIMARY KEY(student_id)
);
ALTER TABLE student ADD gpa DECIMAL(3, 2);
ALTER TABLE student DROP COLUMN gpa;
DESCRIBE student;
DROP TABLE student;Inserting Data
INSERT INTO student VALUES(1, 'Jack', 'Biology');
INSERT INTO student(student_id, name) VALUES(2, 'Kate'); -- NULL valueUpdating and Deleting Data
UPDATE student
SET major = 'Bio'
WHERE major = 'Biology';
UPDATE student
SET name = 'Tom', major = 'Undecided'
WHERE student_id = 1;
-- AND, OR, <>, =, >, <, <=, >=
DELETE FROM student
WHERE student_id = 5;Basic Queries
SELECT student.name, student.major
FROM student
WHERE major = 'Biology' AND name IN ('Claire', 'Kate', 'Mike')
ORDER BY name, major DESC
LIMIT 2;Creating More Complex Tables
CREATE TABLE branch (
branch_id INT PRIMARY KEY,
branch name VARCHAR (40),
mgr_id INT,
mgr_start_date DATE,
FOREIGN KEY(mgr_id) REFERENCES employee(emp_id) ON DELETE SET NULL
);CREATE TABLE works_with (
emp_id INT,
client_id INT,
total_sales INT,
PRIMARY KEY(emp_id, client_id),
FOREIGN KEY(emp_id) REFERENCES employee(emp_id) ON DELETE CASCADE,
FOREIGN KEY(client_id) REFERENCES client(client_id) ON DELETE CASCADE
);More Basic Queries
SELECT first_name AS forename, last_name AS surname
FROM employee;
SELECT DISTINC sex
FROM employee;
SELECT COUNT(emp_id)
FROM employee
WHERE sex = 'F' AND birth_day > '1970-01-01';
SELECT AVG(salary)
FROM employee
WHERE sex = 'M';
SELECT SUM(salary)
FROM employee
WHERE sex = 'M';
SELECT COUNT(sex), sex
FROM employee
GROUP BY sex;
SELECT SUM(total_sales), emp_id
FROM works_with
GROUP BY emp_id;Wildcards
-- % = any # characters, _ = one character
SELECT *
FROM client
WHERE client_name LIKE '%LLC';
SELECT *
FROM branch_supplier
WHERE supplier_name LIKE '% Label%';
SELECT *
FROM employee
WHERE birth_date LIKE '____-10%';Union
SELECT first_name
FROM employee
UNION
SELECT branch_name
FROM branch;Join
SELECT employee.emp_id, employee.first_name, branch.branch_name
FROM employee
JOIN branch
ON employee.emp_id = branch.mgr_id;
-- INNER JOIN, LEFT JOIN, RIGHT JOIN, FULL JOINNested Queries
SELECT employee.first_name, employee.last_name
FROM employee
WHERE employee.emp_id IN (
SELECT works_with.emp_id
FROM works_with
WHERE works_with.total_sales > 30000
);
SELECT client.client_name
FROM client
WHERE client.branch_id = (
SELECT branch.branch_id
FROM branch
WHERE branch.branch_id = 102
);
SELECT a.id, a.name, p.product_name
FROM TableA a
JOIN (
SELECT product_id, product_name
FROM products
WHERE price > 100
) p ON a.id = p.product_id;On Delete
This feature sets the behavior of foreign keys when the original record (REFERENCE) value is deleted.
CREATE TABLE works_with (
emp_id INT,
client_id INT,
total_sales INT,
PRIMARY KEY(emp_id, client_id),
FOREIGN KEY(emp_id) REFERENCES employee(emp_id) ON DELETE CASCADE,
FOREIGN KEY(client_id) REFERENCES client(client_id) ON DELETE CASCADE
);Triggers
DELIMITER $$
CREATE
TRIGGER my_trigger BEFORE INSERT
ON employee
FOR EACH ROW BEGIN
INSERT INTO trigger_test VALUES('added new employee');
-- NEW.first_name
END$$
DELIMITER ;
-- DROP TRIGGER my_triggerEntity Relationship Diagrams (ERD)
- Entity - An object we want to model and store information about
- Attributes - Specific pieces of information about an entity
- Primary Key - An attribute(s) that uniquely identify an entry in the database table
- Composite Attribute - An attribute that can be broken up into sub-attributes
- Multi-valued Attribute - An attribute that can have more than one value
- Derived Attribute - An attribute that can be derived from the other attributes
- Multiple Entities - You can define more than one entity in the diagram
- Relationships - defines a relationship between two entities
- Total Participation - All members must participate in the relationship
- Relationship Attribute - An attribute about the relationship
- Relationship Cardinality - the number of instances of an entity from a relation that can be associated with the relation (1:1, 1:N, N:M)
- Weak Entity - An entity that cannot be uniquely identified by its attributes alone
- Identifying relationship - A relationship that serves to uniquely identify the weak entity
Converting ER Diagrams to Schemas
- Step 1: Mapping of Regular Entity Types - For each regular entity type create a relation (table) that includes all the simple attributes of that entity.
- Step 2: Mapping of Weak Entity Types - For each weak entity type create a relation (table) that includes all simple attributes of the weak entity.
- Step 3: Mapping of Binary 1:1 Relationship Types - Include one side of the relationship as a foreign key in the other Favor total participation.
- Step 4: Mapping of Binary 1:N Relationship Types - Include the 1 side’s primary key as a foreign key on the N side relation (table).
- Step 5: Mapping of Binary M:N Relationship Types - Create a new relation (table) who’s primary key is a combination of both entities primary key’s. Also include any relationship attributes.
Other Use Cases
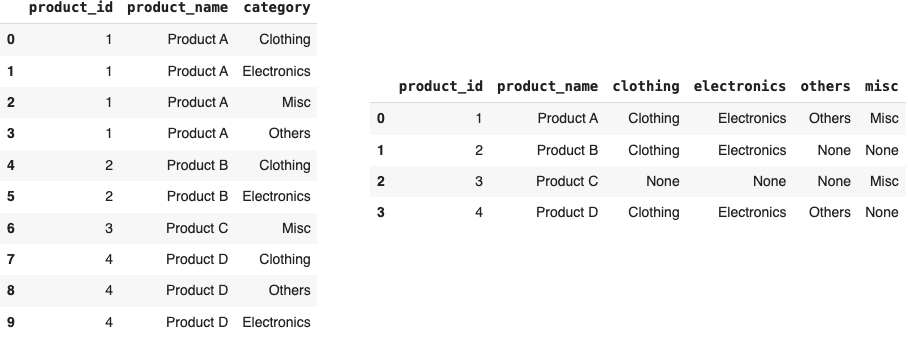
’Duplicated’ Rows With Categories to Only One Single Record
SELECT
product_id,
product_name,
MAX(CASE WHEN category = 'Clothing' THEN category END) AS clothing,
MAX(CASE WHEN category = 'Electronics' THEN category END) AS electronics,
MAX(CASE WHEN category = 'Others' THEN category END) AS others,
MAX(CASE WHEN category = 'Misc' THEN category END) AS misc
FROM products
GROUP BY product_id, product_name;