Motivation
On a traditional supervised machine learning problem using structured and tabular data, often we have to create a model based on a previous dataset. The model must learn and then map the independent variables (features) into a dependent variable (target) . This problem can be represented as a system of linear equations as shown below:
Solve the system of linear equations for .
System Types
- Complete - Non-Singular (Unique Solution)
- Redundant - Singular (Infinite Solutions)
- Contradictory - Singular (No Solution)
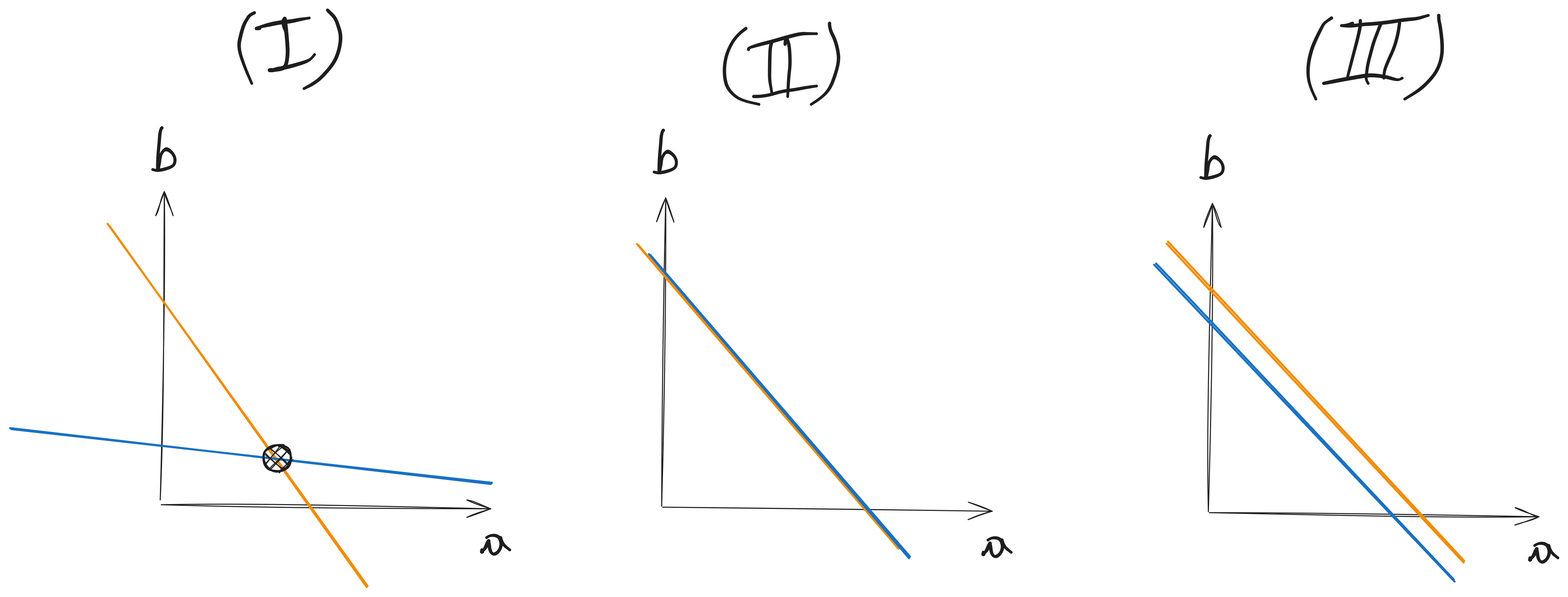
Linear Dependence and Independence
Determinant
If the , then the matrix is non-singular. Also, the determinant can be interpreted geometrically as the area or volume of a linear transformation basis.
Determinant of a Product
Determinant of Inverse
Determinant of Identity
Elementary Row Operations (EROs)
- Switch rows
- Multiply row by a (non-zero) scalar
- Add a row to another row
Row Echelon Form (REF)
- Zero rows are at the bottom
- Each row has a pivot (leftmost non-zero entry)
- Every pivot is to the right of the pivots on the rows above
- Rank of the matrix is the number of pivots
Reduced Row Echelon Form (RREF)
- The matrix must be in row echelon form
- Each pivot is a
- Any number above the pivot has to be
- Rank of the matrix is the number of pivots
Rank
The rank of a matrix can be seen as a measure of the information amount present on a system. It can be interpreted as the number of linear independent equations that make up a system.
If a matrix have a full rank, it means the rank is equal to the matrix order ( for ), then the system is non-singular.
The rank of a matrix can be calculated based on the number of pivots in the row echelon form.
Gaussian Elimination Algorithm
Is a method for row reduction and so for solving linear systems.
- Create the augmented matrix
- Get the matrix into reduced row echelon form
- Complete back substitution
- Stop if you encounter a row of zeros (singular system)
Augmented Matrix
Matrix Inverse
Analogous to a number multiplicative inverse, a square matrix is invertible (also non-singular) if there exists an square matrix such that:
where denotes the identity matrix.
- A matrix is invertible only if .
Identity Matrix
The identity matrix of size is the square matrix with ones on the main diagonal and zeros elsewhere. Analogous to multiplying a number by , the multiplied object remains the same.