It operates by incrementally learning patterns and identifying unexpected events in dynamic environments. Is a unsupervised and adaptative method with a algorithmic complexity .
Based on two strategies:
- GWR: Grow When Required
- SOM: Self-Organizing Maps
Main parameters:
- : Changes the cluster centroid
- : Controls the Gaussian spread
- : Sigma adaptation for each specific cluster
In the context of Markov Chains each cluster defined by a Gaussian represents one possible state on the chain.
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import seaborn as sns
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from ucimlrepo import fetch_ucirepo
sns.set_theme()data = np.array(
[
[5, 5],
[5.2, 4.8],
[4.7, 5.3],
[10, 10],
[10.2, 9.8],
[9.7, 10.3],
[5, 5],
]
)
dataarray([[ 5. , 5. ],
[ 5.2, 4.8],
[ 4.7, 5.3],
[10. , 10. ],
[10.2, 9.8],
[ 9.7, 10.3],
[ 5. , 5. ]])
def get_closest_gaussian(example, centroids, sigma, threshold=1e-3):
"""Find the closest Gaussian cluster from the example point. If no clusters
have been created the function return -1."""
# check if there is no centroids
if centroids.size == 0:
return -1
euclidian_distance = np.apply_along_axis(
lambda center: (np.sum((center - example) ** 2)) ** (1 / 2),
1,
centroids,
)
activation = np.exp(-(euclidian_distance**2) / (2 * sigma**2))
idx = activation.argmax()
# manages the sensitivity for new clusters creation
if activation[idx] < threshold:
return -1
return idx
def estimate_markov_chain_entropy_rate(adj_mat: np.array) -> float:
"""Calculates the Shannon entropy for a Markov Chain given your
adjacency matrix representation."""
return -1 * np.sum(adj_mat * np.log2(adj_mat))
def sonde(X, alpha=0.01, sigma=1, eps=1e-7, delta=0.01, verbose=True):
d = X.shape[1]
centroids = np.empty((0, d))
old_pos = -1
curr_pos = -1
markov = None
old_H = -1
curr_H = -1
H = []
delta_H = []
for point in X:
example = point.reshape(1, d)
curr_pos = get_closest_gaussian(example, centroids, sigma)
if curr_pos == -1:
# create a new Gaussian
if centroids.size == 0:
centroids = np.concatenate((centroids, example), axis=0)
curr_pos = 0
markov = np.array([[eps]])
else:
centroids = np.concatenate((centroids, example), axis=0)
curr_pos = centroids.shape[0] - 1
if centroids.shape[0] > 1:
markov = np.pad(
markov,
((0, 1), (0, 1)),
mode="constant",
constant_values=eps,
)
else:
# adapt an existing Gaussian
centroids[curr_pos, :] = (1 - alpha) * centroids[
curr_pos, :
] + alpha * example
if old_pos != -1:
markov[old_pos, curr_pos] = markov[old_pos, curr_pos] + delta
if verbose:
print(f"Moved from state ( {old_pos} ) to ( {curr_pos} )")
# normalize the adjacency matrix
for i in range(markov.shape[0]):
markov[i] = markov[i, :] / sum(markov[i, :])
# calculate the entropy
curr_H = estimate_markov_chain_entropy_rate(markov)
H.append(curr_H)
# calculate the entropy difference
if old_H != -1:
delta_H.append(curr_H - old_H)
if verbose:
print(f"Markov Adjacency Matrix:\n{markov}")
print("-" * 50)
old_pos = curr_pos
old_H = curr_H
return delta_H, H, centroids, markovdH, H, centroids, markov = sonde(X=data, verbose=True)Markov Adjacency Matrix:
[[1.]]
--------------------------------------------------
Moved from state ( 0 ) to ( 0 )
Markov Adjacency Matrix:
[[1.]]
--------------------------------------------------
Moved from state ( 0 ) to ( 0 )
Markov Adjacency Matrix:
[[1.]]
--------------------------------------------------
Moved from state ( 0 ) to ( 1 )
Markov Adjacency Matrix:
[[0.99009891 0.00990109]
[0.5 0.5 ]]
--------------------------------------------------
Moved from state ( 1 ) to ( 1 )
Markov Adjacency Matrix:
[[0.99009891 0.00990109]
[0.4950495 0.5049505 ]]
--------------------------------------------------
Moved from state ( 1 ) to ( 1 )
Markov Adjacency Matrix:
[[0.99009891 0.00990109]
[0.49014802 0.50985198]]
--------------------------------------------------
Moved from state ( 1 ) to ( 0 )
Markov Adjacency Matrix:
[[0.99009891 0.00990109]
[0.49519606 0.50480394]]
--------------------------------------------------
centroidsarray([[ 4.9989902, 5.0010098],
[ 9.99898 , 10.00102 ]])
Time Series Data Example
# fetch dataset
toy_data = fetch_ucirepo(id=849)
toy_data = pd.DataFrame(
toy_data.data.targets["Zone 1 Power Consumption"]
).valuesdH, H, centroids, markov = sonde(
X=toy_data, verbose=False, sigma=1000, delta=0.08
)print(
f"Total Number of Gaussians: {len(centroids)}\n\nCentroids:\n\n{centroids}"
)Total Number of Gaussians: 11
Centroids:
[[33312.57309826]
[30891.4939403 ]
[28318.79031478]
[25022.61994598]
[36808.20341654]
[39446.49818873]
[22225.51194093]
[13963.59379581]
[44080.06259361]
[46417.1414591 ]
[20081.03920279]]
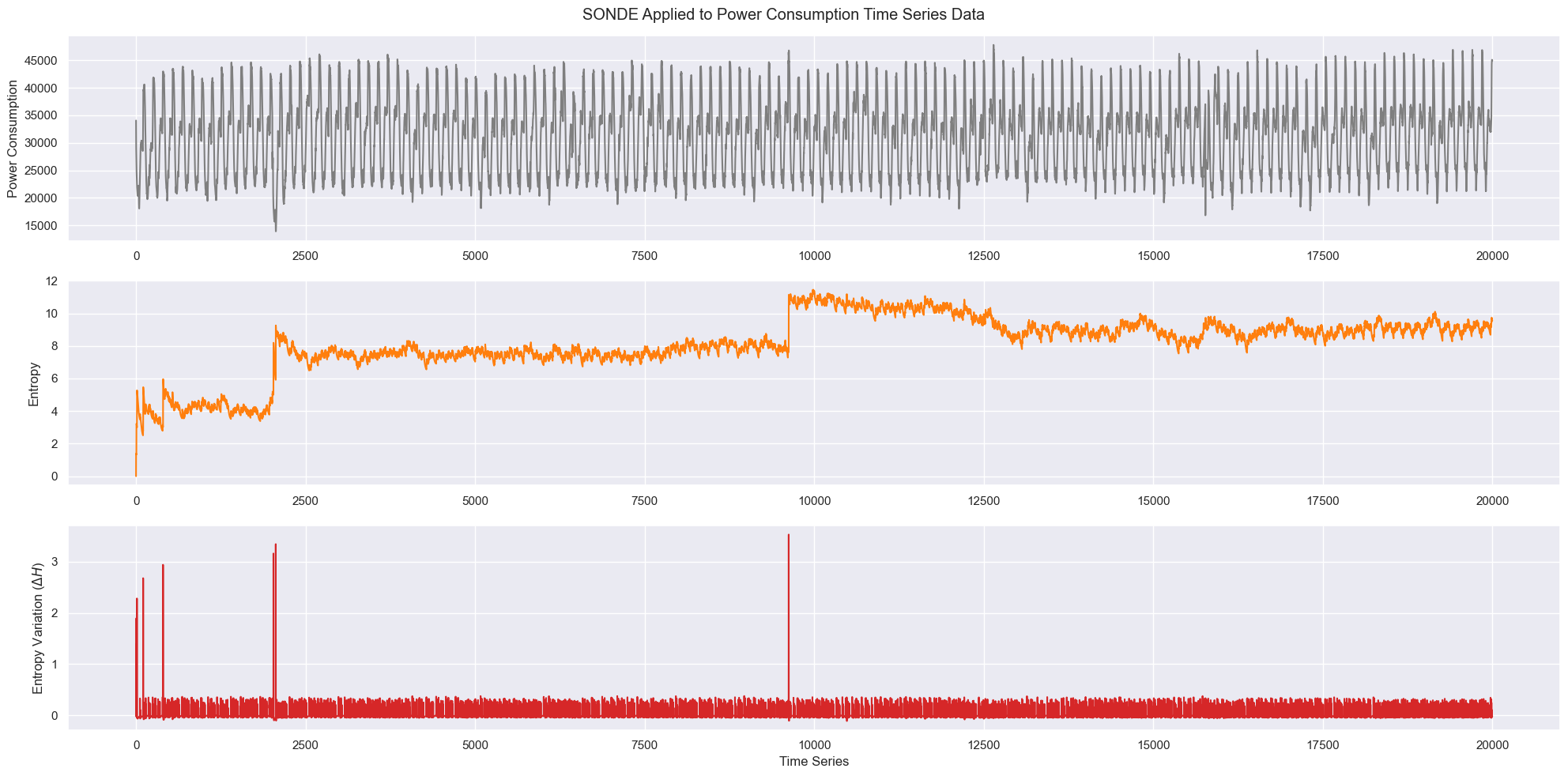
fig, (ax1, ax2, ax3) = plt.subplots(3, figsize=(20, 10))
fig.suptitle("SONDE Applied to Power Consumption Time Series Data")
ax1.plot(toy_data[:20000, :], "tab:gray")
ax2.plot(H[:20000], "tab:orange")
ax3.plot(dH[:20000], "tab:red")
ax1.set_ylabel("Power Consumption")
ax2.set_ylabel("Entropy")
ax3.set_ylabel(r"Entropy Variation ($\Delta H$)")
ax3.set_xlabel("Time Series")
fig.tight_layout();